There are 2 key studies carried out in Italy at the peak of the first wave of the Covid pandemic.
The results of both studies demonstrate that there is a benefit in adding in this novel Probiotic blend, Sivomixx in the outcome of Covid patients, in terms of respiratory effects and mortality.
Both studies have now been published and are attached.
There are 3 attachments
Summary slides of the 2 presentations
The role of probiotics in the Gut/Lung axis has been demonstrated in a number of studies, one of which is attached for your information.
A new formulation, known as Sivomixx, is a multi-strain, high dose probiotic formulation. has been studied in patients infected with Covid. There are 2 studies which I would like to bring to your attention.
Study 1
This study took place in Italy at the height of the Covid outbreak, between 9th March and 4th April, and was a hospital based where 70 patients were randomised into 2 groups.
The first group of 42 received a combination of Hydroxychloroquine, antibiotics and tocilizumab, the 2nd group of 28 had Sivomixx added, 3 times a day of 800 bn concentration per dose.
The results showed ‘The estimated risk of developing respiratory failure was eight fold lower in the group receiving Sivomixx’ it also demonstrated that a large proportion (43%) of those treated with Sivomixx had resolution of diarrhoea with 24 hours and 93% within 3 days.
Please also see attached link to the press release below:
Study 2 was even more interesting
This was carried out in Italy between 6 March and April 26, and involved 200 patients who all received the Best Available Therapy (BAT) at the time which was a combination of hydroxychloroquine 200mg bd for 7 days, azithromycin 500mg od for 7 days, tocilizumab, low molecular weight heparin, and either lopinavir-ritonavir (400mg/100mg) bd, or darunavir–cobicistat (800/150 mg) od for 14 days and tocilizumab.
Of the 200 patients, 112 received the above BAT regimen, the remaining 88 received BAT and Sivomixx in a dose of 800bn 3 times a day. The Sivomixx was given within one day from admission and continued for whilst patients remained in ITU.
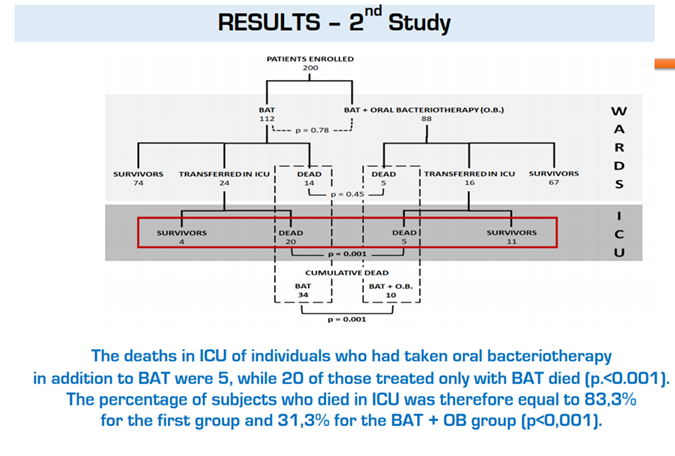
The primary end point was mortality and demonstrated a reduction in mortality in the group given the Sivomixx than in the BAT group alone.
